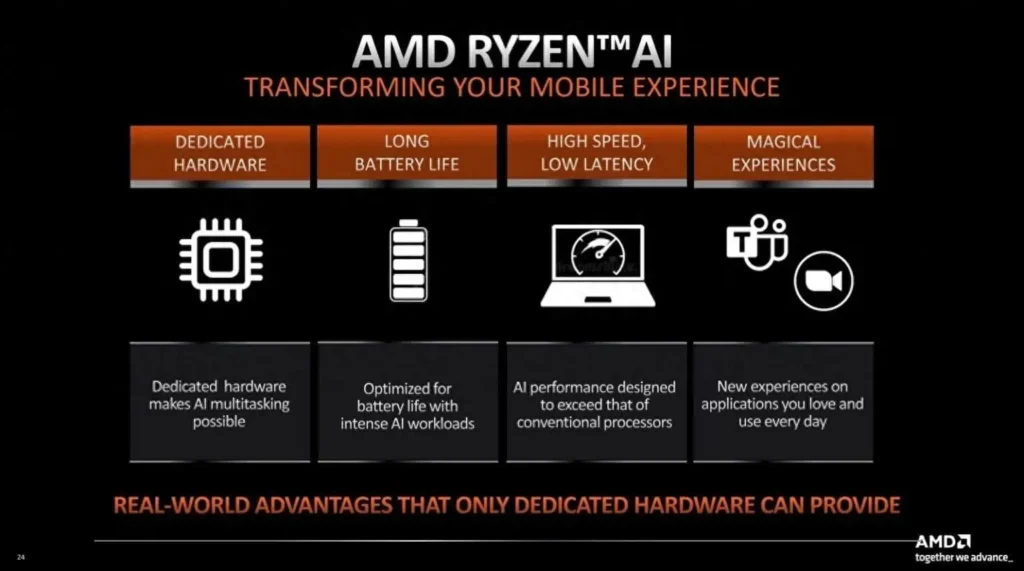
Recently, the editor has shared a lot of leaks about the next-generation processors from Intel and AMD. One of the biggest and most noteworthy changes is that both companies will include artificial intelligence (AI) computing units in their consumer-grade processors in the future.
In addition, there is another related news that Microsoft’s next-generation Windows 12 operating system will be rebuilt using artificial intelligence. Previously, there were rumors that Microsoft’s “next-generation” operating system referred to Windows 12, which would be released in June this year.
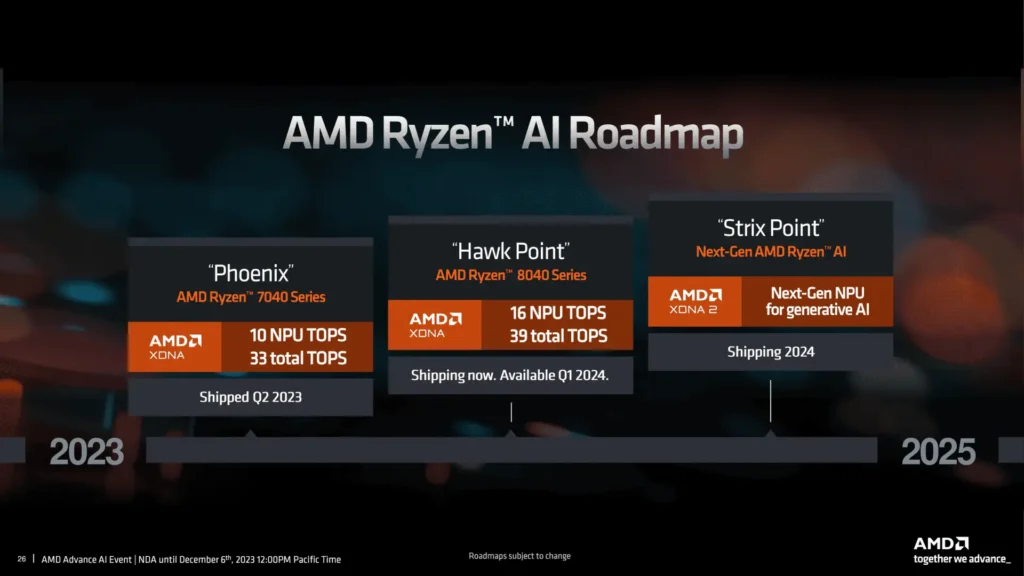
However, some time ago, Microsoft’s official website published an article, clearly stating that it will release Windows 11 24H2 within the year, without mentioning Windows 12. Therefore, the possibility of Microsoft releasing the Windows 12 operating system within the year is very small, almost nonexistent. Despite this, it is rumored that Windows 11 24H2 will also add a large number of features related to artificial intelligence.
From the current known signs, around 2025 will be the first year of the popularization of artificial intelligence in consumer computing devices, whether it is processors or operating systems, both will be reconstructed by artificial intelligence.
Seeing this, some friends may have some doubts in their hearts: Are these just gimmicks concocted and hyped by manufacturers? Are they really practical? The editor himself had such doubts before.
—But now, the editor tells everyone very seriously and responsibly: These are not gimmicks, and soon, the vast majority of computer users will be able to truly experience and perceive them.
Speaking of the Windows Task Manager, computer users are very familiar with it. In this built-in small program of the system, users can intuitively see the real-time usage of hardware resources including processors, memory, hard drives, network cards, and graphics cards.
The main types of hardware displayed by the Windows Task Manager are just those mentioned above, but this situation will undergo significant changes in the upcoming Windows 11 24H2, with the addition of a new type of hardware resource usage and monitoring information, which is the AI computing unit NPU.

AMD recently confirmed this news, stating that it is cooperating with Microsoft to implement the aforementioned function. Through the use of the Compute Driver Model (CDM) interface, the future Windows 11 operating system will be able to monitor the usage and related information of AMD’s XDNA NPU, including power usage, and more.
AMD stated that adding NPU usage monitoring in the Microsoft Windows operating system Task Manager is very important for the future, as it can make software development easier and improve device optimization for users, such as maximizing battery life.
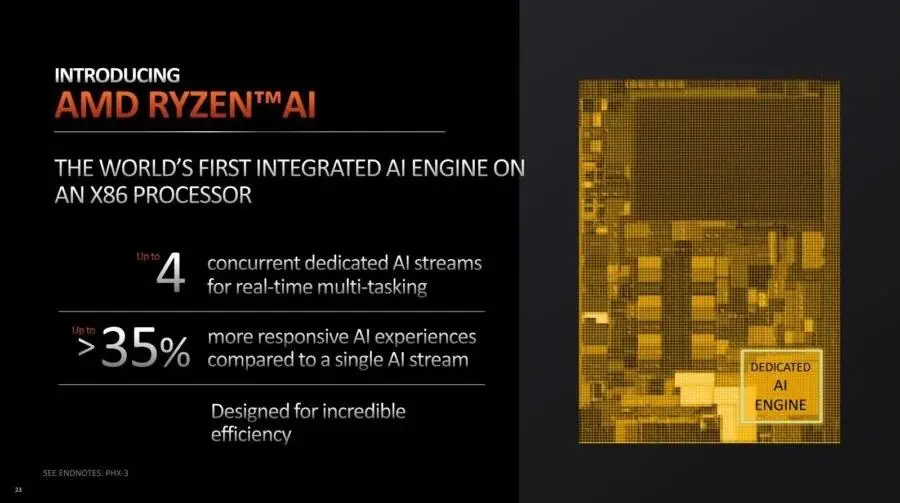
Despite this, AMD is still behind its old rival Intel in this respect, as Intel’s new processors with integrated NPU units already support this feature, please refer to the picture above.
Current AI applications can be roughly divided into two categories. One is very large in scale and requires extremely high computing power. These projects are generally deployed in dedicated data centers, equipped with a massive number of AI computing cards.
The other is lightweight AI applications, which can be deployed on users’ local computers, such as the Chat with RTX released by Nvidia a few days ago, please refer to the picture above.
Users can submit various files to the application, and Chat with RTX can automatically analyze, and organize the data modeling inside the files, and then users can ask questions in a natural language chat manner, querying related results, with a user experience similar to ChatGPT and Wenxin Yiyan.
These types of AI applications do not require high hardware computing power, so the future consumer computing devices equipped with AI computing units are not gimmicks, have considerable practical value, and are still in the early stages of development, with infinite possibilities in the future.
In summary, when consumer-grade processors are equipped with AI processing units and the Windows operating system Task Manager also adds NPU usage monitoring, it essentially marks the real popularization of artificial intelligence in consumer computing devices. The editor personally predicts that this situation will become a reality around 2025.









