When choosing a solid-state drive (SSD), we often encounter terms like M.2, PCIe, and NVMe. Although these terms frequently appear together, sometimes one may be supported while the other is not. These three terms actually represent different aspects of an SSD, so it’s important to understand them before purchasing to avoid spending money without experiencing the expected performance.
01
M.2: A New Form Factor for Interfaces and Appearance

M.2, originally named Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF), is a connector interface standard designed for compact devices. It was released by the PCI-SIG association and aims to support multiple modules/cards on the same connector. In addition to SSDs, M.2 interfaces are also used for Wi-Fi modules, Bluetooth devices, and other components.
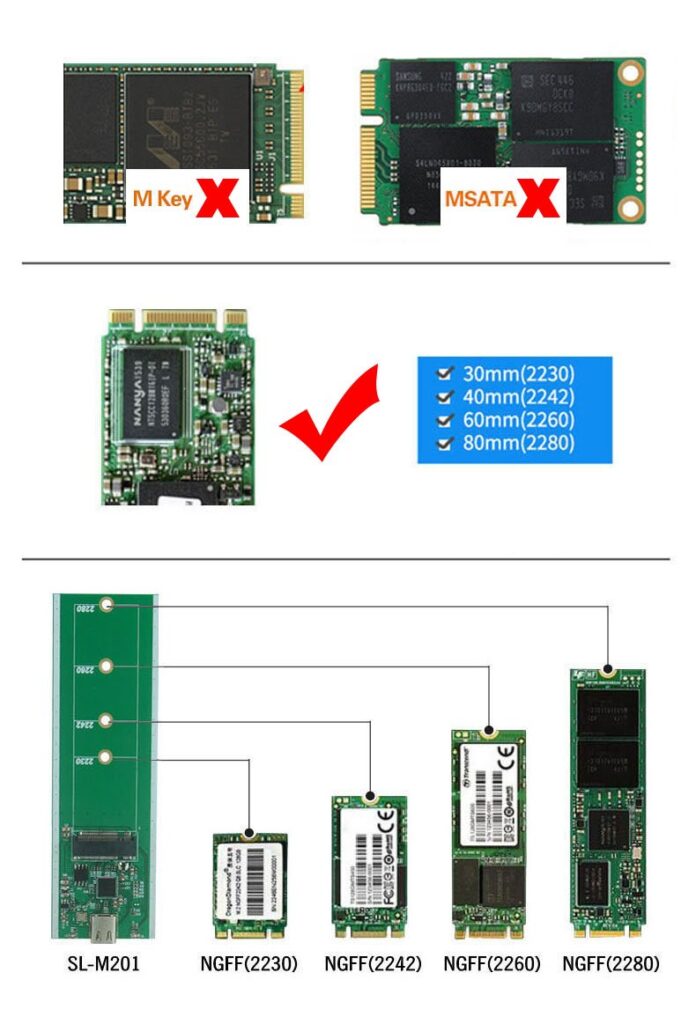
There are three types of M.2 interfaces: M-Key, B&M-Key, and B-Key. The M-Key interface supports PCI-E x4 channels with a bandwidth of up to 32Gbps, while the B-Key interface mainly supports SATA and PCI-E x2 channels.
M.2 interfaces are commonly used in laptops and motherboards. Compared to traditional SATA interfaces, they save a significant amount of space, allowing SSDs to be easily installed on the motherboard. M.2 solid-state drives typically come in five sizes: 2230, 2242, 2260, 2280, and 22110. The “22” refers to a width of 22 millimeters, while the number following it indicates the length of the SSD.
02
PCIe: A High-Speed Data Transfer Channel

PCIe, or Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard. It replaced older PCI and AGP bus standards and has become the mainstream interface for connecting high-speed components to motherboards. Besides SSDs, PCIe is also used by graphics cards, sound cards, network cards, and other devices.
The PCIe bus offers extremely high data transfer rates. For example, a PCIe 4.0 x4 channel can achieve transfer speeds of over 7000MB/s, nearly double the rate of PCIe 3.0 x4. Additionally, PCIe uses a point-to-point connection, meaning each device is assigned its own dedicated bandwidth without sharing the bus bandwidth, thus improving data transfer efficiency and reliability.
It’s important to note that there are slots on motherboards also labeled as PCIe. These slots use the same PCIe bus, meaning PCIe-compatible SSDs can also be used with a PCIe interface through an adapter card, allowing M.2 PCIe SSDs to be compatible.
03
NVMe: A High-Performance Storage Protocol
NVMe, which stands for Non-Volatile Memory Express, is a storage protocol created from the ground up for performance. It is specifically designed for non-volatile memory such as NAND flash and operates over high-speed PCIe channels. The NVMe protocol can be considered a protocol exclusive to SSDs, as any SSD labeled with NVMe is guaranteed to be a solid-state drive.
NVMe allows direct communication with the system’s CPU, resulting in extremely low latency. It also supports 64K command queues, with each queue capable of holding up to 64K commands, significantly enhancing SSD IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) performance. Additionally, NVMe includes features like automatic power state switching and dynamic energy management, which effectively reduce power consumption.
In summary, M.2 defines the interface and form factor of an SSD, but an SSD using the M.2 interface may not necessarily support the NVMe protocol. The NVMe protocol allows SSDs to fully utilize their high-speed read and write capabilities, and all NVMe-based SSDs use the PCIe bus for data transfer. PCIe, in turn, provides the high-speed data transfer channel for the SSDs.

Disclaimer:
- This channel does not make any representations or warranties regarding the availability, accuracy, timeliness, effectiveness, or completeness of any information posted. It hereby disclaims any liability or consequences arising from the use of the information.
- This channel is non-commercial and non-profit. The re-posted content does not signify endorsement of its views or responsibility for its authenticity. It does not intend to constitute any other guidance. This channel is not liable for any inaccuracies or errors in the re-posted or published information, directly or indirectly.
- Some data, materials, text, images, etc., used in this channel are sourced from the internet, and all reposts are duly credited to their sources. If you discover any work that infringes on your intellectual property rights or personal legal interests, please contact us, and we will promptly modify or remove it.








