Whether it is a solid-state drive or a mechanical hard drive when installing a system, we encounter an option: should the hard drive use MBR or GPT partitioning? MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (GUID Partition Table) are two mainstream hard drive partitioning schemes, each with its pros and cons, but they cannot be chosen arbitrarily. Therefore, it is necessary to understand their differences.
| MBR | GPT | |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum partition capacity | 2TB | 9.4zb (1zb=1 billion TB) |
| Maximum number of partitions | 4 primary partitions (or 3 primary partitions and an unlimited number of logical partitions) | 128 primary partitions |
| Supported firmware interfaces | BIOS | UEFI |
| Supported operating systems | Windows 7 or earlier systems Windows 95/98/XP/2000 | Newer systems such as Windows 10 32-bit; Windows 8/8.1/10 64-bit |
01
MBR: The Guardian of Traditional Hard Drives
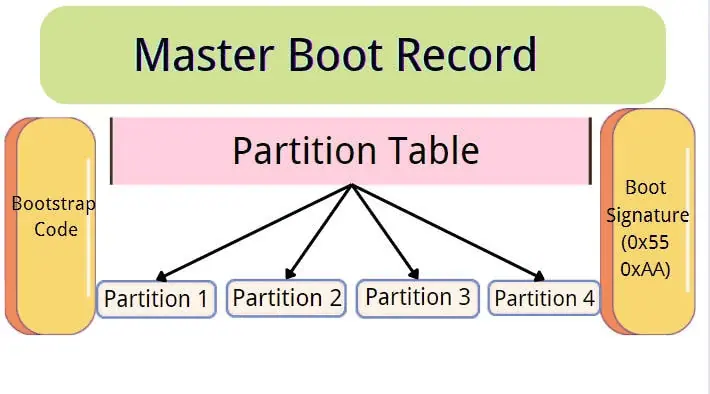
MBR (Master Boot Record) is a traditional hard drive partitioning mode that has been widely used since the advent of the IBM PC-compatible machine. The MBR partition table is located in the first sector of the hard drive, occupying 512 bytes, with the first 446 bytes used to store the boot loader, the next 64 bytes for storing partition table information, and the last two bytes as the partition table’s validity flag.
Due to the limited computer performance and disk space at the time of MBR’s creation, it has many limitations. MBR supports a maximum hard drive capacity of 2TB and can only create 4 primary partitions. If more partitions are needed, an extended partition must be established under which logical partitions can be created. This structure is relatively complex, but MBR has excellent compatibility, making it especially suitable for older computer systems that use traditional BIOS booting.
02
GPT: The Leader of Future Hard Drives
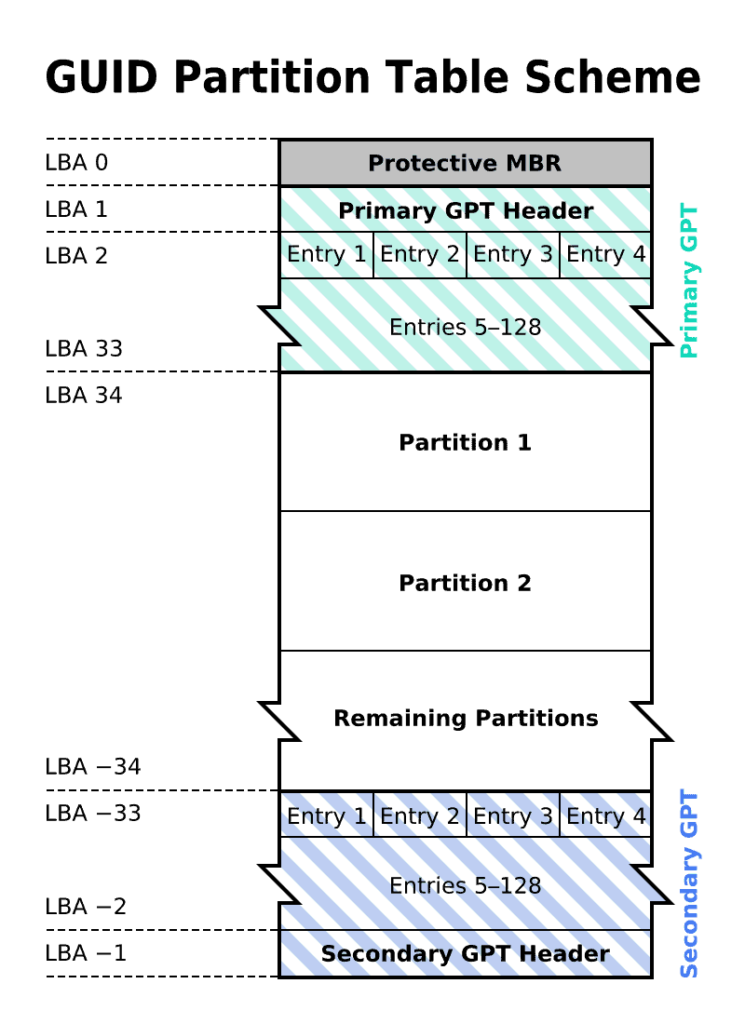
GPT (GUID Partition Table) is a more advanced hard drive partitioning standard introduced with the rise of UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface). GPT uses a series of 64-bit globally unique identifiers (GUIDs) to identify partitions. Its partition information is not limited to a single sector but is distributed across multiple locations on the hard drive, enhancing data security and reliability.
GPT breaks through MBR’s 2TB capacity limit and theoretically supports almost unlimited hard drive space. Under the Windows system, it can directly create 128 partitions, greatly enhancing partition flexibility. Moreover, GPT includes a backup partition table, so even if the primary partition table is damaged, it can be restored from the backup, increasing data security.
03
Clarify Your Needs, Choose the Partition Mode Without Hassle

First of all, it is important to clarify that regardless of whether it is MBR or GPT, the different partition modes almost do not affect the hard drive’s performance. That is, the read/write speed and lifespan of the hard drive will not be impacted by the partition mode. Therefore, you should just consider the platform you are using.
If your computer supports UEFI boot and you seek faster boot speed and more advanced features, GPT is the better choice. Conversely, if you are using a traditional BIOS system, although both MBR and GPT can theoretically be chosen, MBR might be more compatible.
If your hard drive capacity exceeds 2TB, choosing GPT is almost inevitable as it is the only one that can fully utilize the space of large-capacity hard drives. Considering possible future system upgrades or hardware replacements, GPT is recommended in the long run due to its advanced nature and expandability, especially for users who are buying a new computer or planning a major system upgrade.

Disclaimer: This article is created by the original author. The content of the article represents their personal opinions. Our reposting is for sharing and discussion purposes only and does not imply our endorsement or agreement. If you have any objections, please get in touch with us through the provided channels.