Electronic circuits are easily damaged in cases of overvoltage, overcurrent, surges, etc. With the development of technology, electronic circuit products are becoming increasingly diverse and complex, making circuit protection particularly important. Circuit protection components have also evolved from simple glass tube fuses to a wider variety with superior protective performance.
The significance of circuit protection?”
“In various electronic devices, the significance of overvoltage and overcurrent protection has increasingly grown. So, what exactly is the significance of circuit protection? Let’s delve into it today:
(1) Due to the increasing integration level of circuit boards nowadays, the prices of these boards have risen significantly. Hence, it’s essential to enhance protection.
(2) Semiconductor devices and ICs are exhibiting a trend towards lower operating voltages. The purpose of circuit protection is to reduce energy consumption losses, minimize heat generation, and extend the lifespan of these devices.
(3) In vehicular equipment, conditions are harsher compared to typical electronic products. As cars experience various driving conditions, there are significant momentary voltage peaks during vehicle startup. Therefore, power adapters for these electronic devices generally require overvoltage protection components.
(4) Communication equipment demands a certain level of protection against lightning surges. The use of overvoltage and overcurrent protection components becomes crucial in these devices as they are key to ensuring user safety and normal communication.
(5) Most malfunctions in electronic products stem from overvoltage or circuit phenomena within the electronic device circuits. As our expectations for electronic device quality increase, electronic circuit protection becomes even more crucial and cannot be overlooked.
Given the significance of circuit protection, let’s introduce several commonly used circuit protection components today.
01
Surge Protection Devices
① Ceramic Gas Discharge Tubes:
The most widely used surge protection device in lightning protection is the ceramic gas discharge tube. Its widespread application stems from its effectiveness in lightning protection for both DC power sources and various signals. Its key features include high current-carrying capacity, low inter-stage capacitance, high insulation resistance, and a wide range of breakdown voltages.
② Semiconductor Surge Arresters:
A type of overvoltage protection device, the semiconductor surge arrester operates based on the thyristor principle. It triggers conduction and discharge through the breakdown current of the PN junction, capable of handling large surge or pulse currents. Its breakdown voltage range determines the extent of overvoltage protection.
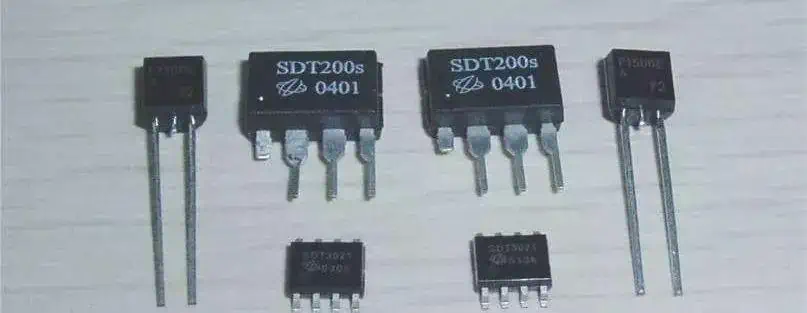
Solid-state surge arresters can be directly connected across the protected circuit terminals. They possess precise conduction, rapid response (response time in nanoseconds), strong surge absorption capability, bidirectional symmetry, and high reliability.
③ Glass Gas Discharge Tubes:
Glass gas discharge tubes (also known as high-performance discharge tubes or lightning protection tubes) emerged as lightning protection devices introduced in the late 20th century. They combine the advantages of ceramic gas discharge tubes and semiconductor overvoltage protectors: high insulation resistance (≥10^8Ω), low inter-stage capacitance (≤0.8pF), high discharge current (up to 3 kA), bidirectional symmetry, rapid response (without delayed breakdown), stable and reliable performance, and low post-conduction voltage.
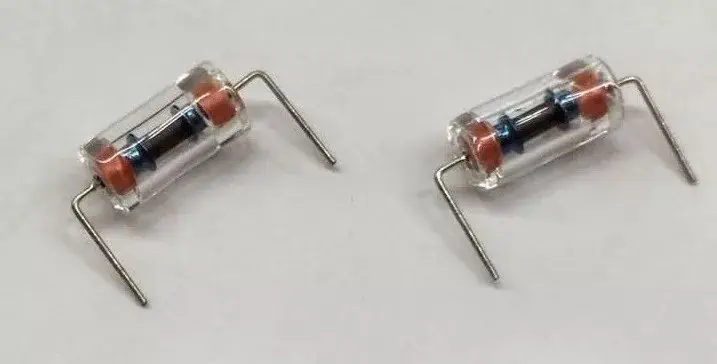
Moreover, they offer high DC breakdown voltages (up to 5000V), small size, and long lifespan. However, a drawback lies in their relatively large DC breakdown voltage dispersion (±20%).
02
Overvoltage Protection Devices
① Varistors (VDRs – Voltage Dependent Resistors):
Varistors are widely used as voltage-limiting devices. Utilizing the nonlinear characteristics of varistors, when overvoltage occurs across the varistor’s terminals, it clamps the voltage to a relatively fixed value, thereby safeguarding subsequent circuits.

The response time of varistors is in the nanosecond range, faster than gas discharge tubes but slightly slower than TVS diodes. Typically employed in overvoltage protection for electronic circuits, their response speed meets the requirements. The junction capacitance of varistors generally ranges from hundreds to thousands of pF. In many cases, they are not suitable for direct application in the protection of high-frequency signal lines. When applied in AC circuits, their large junction capacitance may increase leakage current, necessitating careful consideration in protective circuit design. While varistors have high current-carrying capacity, it is smaller compared to gas discharge tubes.
② Role of Surface Mount Varistors:
Surface mount varistors are primarily used to protect components and circuits, preventing Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) occurrences in power supplies, control, and signal lines.

③ Transient Voltage Suppression Diodes (TVS Diodes):
TVS diodes are extensively used in protecting semiconductors and sensitive components. They are commonly employed as secondary protection. Usually utilized as secondary protection following ceramic gas discharge tubes, some users directly use them for primary protection in products.

Characteristics of TVS diodes include rapid response (in picoseconds), small size, high pulse power, and low clamping voltage. Their 10/1000μs pulse power ranges from 400W to 30KW, while peak pulse currents range from 0.52A to 544A. Breakdown voltages are available in series from 6.8V to 550V, catering to various circuit voltage requirements.
03
Overcurrent Protection Devices
① Polymeric Positive Temperature Coefficient (PPTC) Resettable Fuses:
The PPTC resettable fuse, also known as a self-recovery fuse, is an overcurrent electronic protection component. It’s created by incorporating conductive particle materials into high-polymer organic polymers through a sulfuration reaction under high pressure, high temperature, and specific processing techniques. The PPTC (Polymeric Positive Temperature Coefficient) is a positive temperature coefficient polymer thermistor used for overcurrent protection and can replace traditional current fuses.
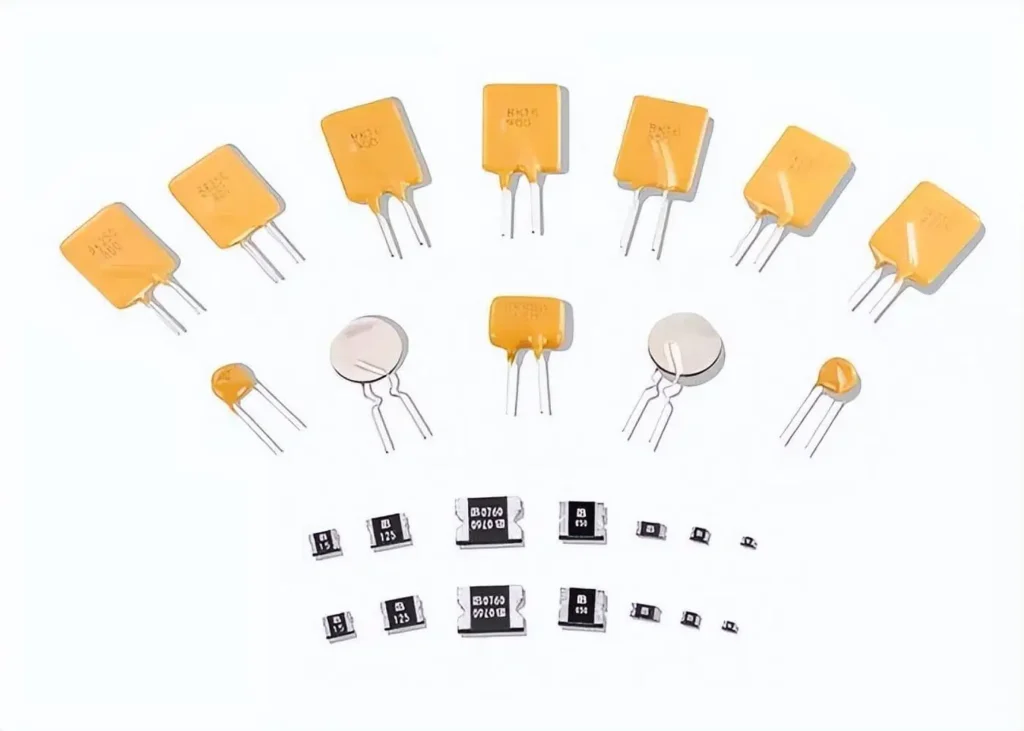
During normal circuit operation, its resistance is minimal (resulting in low voltage drop). However, when the circuit experiences overcurrent, causing an increase in its temperature, its resistance sharply increases by several orders of magnitude. This increase in resistance reduces the current in the circuit to a safe level, thus safeguarding subsequent circuitry. Once the overcurrent ceases, it automatically reverts to its low-resistance state.
04
Electrostatic Components
① ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) Protection Diodes:
ESD protection diodes are overvoltage and static protection components designed for I/O port protection in high-speed data transmission applications. These diodes are utilized to prevent sensitive circuits in electronic devices from being affected by Electrostatic Discharge (ESD).

They offer very low capacitance, excellent Transmission Line Pulse (TLP) testing, and IEC6100-4-2 testing capabilities, particularly enhancing the protection of sensitive electronic components, even after multiple samples up to 1000.
② Role of Inductors:
Understanding the electromagnetic relationship, the role of inductors is crucial in stabilizing circuits during their initial unstable phase. When current passes through an inductor at the circuit’s initial phase, it generates an induced current opposite in direction to the original current flow (Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction). As the circuit operates over time and stabilizes, with no significant changes in current, electromagnetic induction ceases. This stability ensures the circuit’s safety, similar to a waterwheel starting slowly due to resistance and gradually attaining equilibrium.

③ Role of Ferrite Beads:
Ferrite beads possess high resistivity and permeability. They are equivalent to a series connection of resistance and inductance, both of which vary with frequency. They exhibit superior high-frequency filtering characteristics compared to regular inductors. At high frequencies, they display resistive behavior, thus maintaining relatively high impedance across a wide frequency range. This improves frequency modulation filtering effects and finds application in Ethernet chips.


Related: