Time flies, and in a blink, it is already January 2024. It is known that there will be two significant changes in consumer-grade computing devices this year.
- The next-generation processors from Intel and AMD will both incorporate artificial intelligence units.
- Rumors are circulating that Microsoft will release the next-generation Windows 12 operating system in June this year, incorporating AI reconstruction.
As for graphics cards, NVIDIA has long integrated artificial intelligence and high graphic performance. The strides towards this direction will only grow larger in the future, and AMD’s graphics cards will also focus in this direction.
Therefore, it can be said that 2024 will be the true first year of artificial intelligence popularization. AI will no longer be confined to various high-end laboratories or enterprise-level users; it will genuinely enter ordinary households and begin comprehensive popularization.

Artificial intelligence serves various purposes. Many may think of Google’s AlphaGo as it can play Go, surpassing even top human players through trained decision-making and strategic abilities.
Next, there’s the realm of beauty enhancement. Almost all smartphones now feature AI beauty functions, capable of reducing wrinkles, slimming faces, and more. Some may also think of applications like Midjourney, Stable Diffuse, and ChatGPT, where AI is used for painting, composing music, and writing.
However, these are just the tip of the iceberg. The applications of AI go beyond these, extending into significant roles in scientific research.
Recently, Microsoft and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) of the U.S. Department of Energy jointly announced a collaboration. By deeply integrating AI into the research process, they discovered a new battery material. This material, while achieving equivalent performance, reduces lithium content in traditional lithium batteries by 70%.
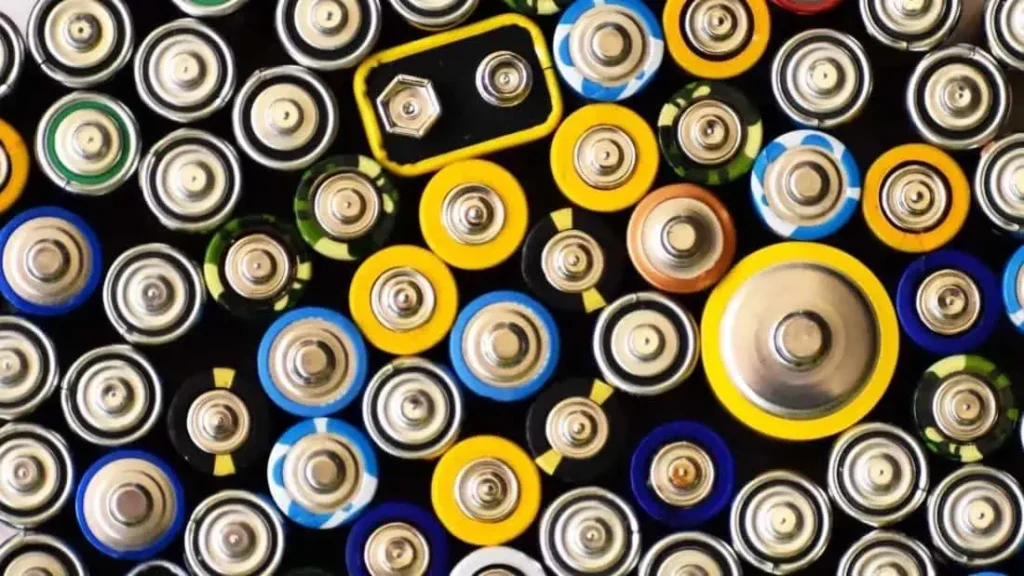

Modern lithium-ion rechargeable batteries, reliant on lithium and other rare-earth metals, boast extended cycling lifespans, making them excellent materials for battery manufacturing. However, lithium batteries also come with significant drawbacks. The efficient recycling of discarded lithium batteries is challenging, leading to potential adverse environmental impacts.
Researchers from Microsoft and PNNL employed high-performance computing systems, utilizing artificial intelligence and the Azure Quantum Elements cloud platform to simulate, predict, and verify various characteristics of new materials. The goal was to identify battery materials with superior properties.
A total of 32.6 million materials were initially screened, with the AI algorithm narrowing it down to 500,000 in the first round. After the second round of selection, candidate materials were further reduced to 800. In the third round, the Microsoft Quantum team used AI to accelerate simulation validation, narrowing down the selection to 150 materials.
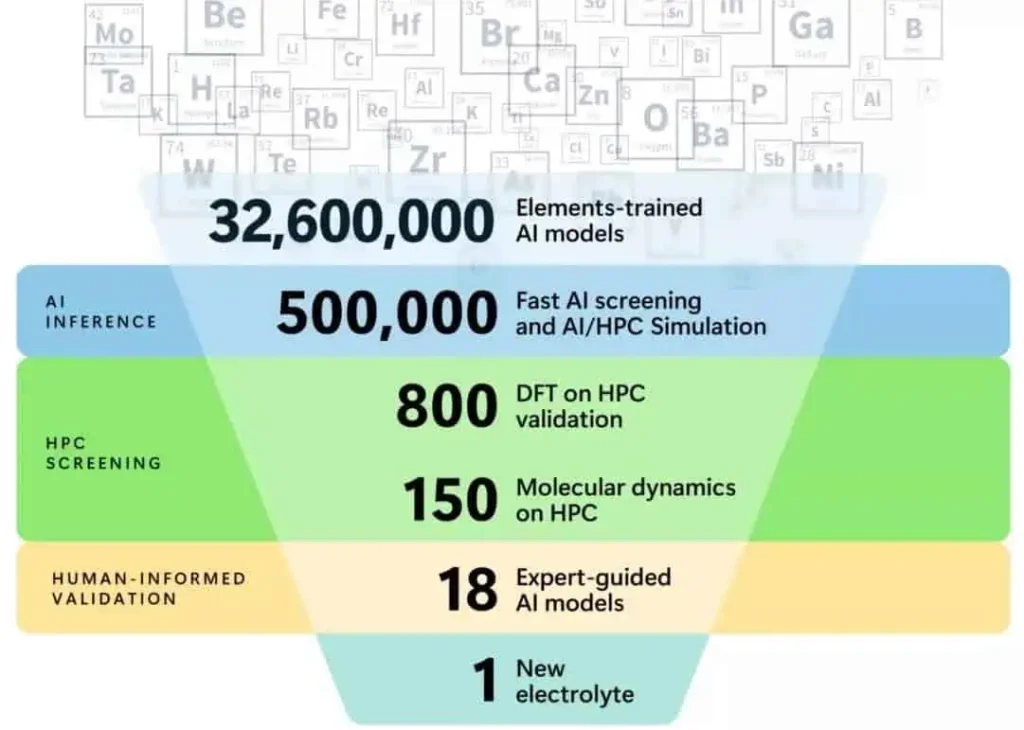
After the fourth round of selection, 18 optimal candidate materials were identified. Ultimately, the research team chose a new electrolyte material with the best comprehensive performance, capable of reducing lithium content in existing lithium-ion batteries by 70%. Moreover, it allows for the partial substitution of lithium with sodium.
During the development and validation process, the team trained an artificial intelligence model with millions of data points. This model, when compared to traditional density functional theory calculations, accelerated the prediction of material properties by 1500 times.
Microsoft stated that by integrating artificial intelligence, the Azure Quantum Elements platform, and existing scientific research methods, the speed of traditional chemical and materials research and development can be increased tenfold. What used to take 250 years for development can now be achieved in just 25 years.
Currently, the team has successfully synthesized this new material and is undergoing further testing to validate its stability and efficiency. With vast commercial prospects, this innovation could make a significant contribution to environmental conservation.
Related:
- Wikipedia No Longer Trusts CNET: AI Misuse Scandal!
- Apple AI Ditches DeepSeek, Partners with Alibaba in China

Disclaimer: This article is created by the original author. The content of the article represents their personal opinions. Our reposting is for sharing and discussion purposes only and does not imply our endorsement or agreement. If you have any objections, please contact us through the provided channels.








