Those who have experienced the era of hard disk drives (HDDs) should know that when an HDD runs slowly, using software to defragment it can improve read and write speeds to some extent. However, does this method also apply to solid-state drives (SSDs) in the same way? Today, let’s understand the role of defragmentation and whether SSDs need it.
01
What is defragmentation?
Defragmentation is the process of organizing and rearranging data on storage devices (such as HDDs) to store it in contiguous blocks. This helps improve the device’s performance and speed.

On an HDD, data is stored on rotating disks called platters. When a file is saved, it is broken into smaller parts called blocks, which are scattered across the platters. When a computer needs to access the file, it must read blocks from different locations on the platters, which can take longer than reading all blocks from a single location. Defragmentation rearranges the file’s blocks to store them together, allowing the computer to access the file more quickly.
02
SSDs do not need defragmentation
Due to the way SSDs operate, the impact of file fragmentation is not as noticeable. SSDs can access data from any location quickly. Storing different data in different storage chips using various storage channels can speed up data retrieval, as the bandwidth of multiple channels and chips is combined.

Although it is possible to run defragmentation routines on SSDs, users are unlikely to notice any performance difference. Moreover, defragmenting an SSD might even be harmful.
03
Disadvantages of defragmenting SSDs
It is not recommended to defragment SSDs because it can reduce their performance and lifespan. SSDs have a limited number of write cycles, and the nature of defragmentation can use a significant portion of these write cycles, leading to decreased performance over time.

Additionally, defragmenting an SSD can be very time-consuming, especially for larger-capacity SSDs. Due to the way SSDs read and write data, defragmentation requires the drive to essentially erase and rewrite data, which can saturate its resources and consume a large amount of cache capacity when writing to flash cells.
04
Better methods to optimize SSDs
Since defragmentation is not advisable for SSDs, how should you correctly optimize your SSD when it feels slow? Generally, SSDs self-optimize, but the following methods can help keep them running at peak speed:
Enable the SSD’s TRIM function. TRIM helps maintain SSD performance by deleting unused data blocks and making them available for reuse, preventing the SSD from becoming cluttered with unused data. The operating system may already silently execute TRIM commands or some more modern equivalent commands.
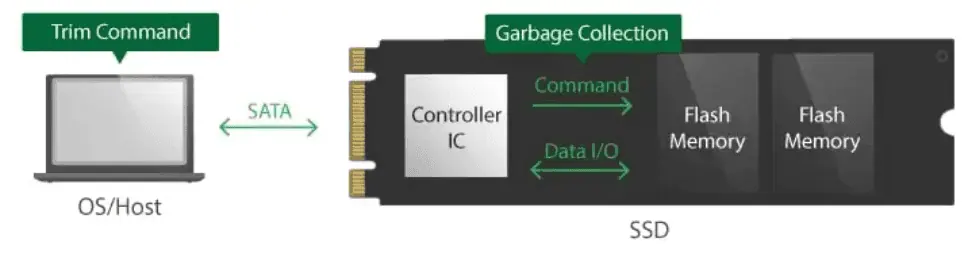
Reserve some OP space. OP space refers to leaving a portion of the SSD’s capacity for the drive’s firmware use. This can help improve the SSD’s performance and lifespan by reducing write cycles and providing extra space for data storage. Most SSDs have built-in OP space, but some manufacturers allow users to modify the reserved space size using specialized applications.
Regularly delete junk files on the SSD. Freeing up space on the SSD can also help improve its performance. This can be done by periodically deleting unused files and uninstalling unnecessary programs.
05
Conclusion
Given the differences in how SSDs and HDDs operate, defragmentation, which has significant optimization benefits for HDDs, does not apply to SSDs. Many methods can improve SSD performance, but defragmentation is not one of them. Even if it does slightly improve performance, it does not justify the time required for defragmentation and the additional wear on the SSD.

Disclaimer: This article is created by the original author. The content of the article represents their personal opinions. Our reposting is for sharing and discussion purposes only and does not imply our endorsement or agreement. If you have any objections, please contact us through the provided channels.








