When purchasing a new computer, have you ever been overwhelmed by the various ports? Don’t worry, today we’ll discuss the dizzying port technologies: Thunderbolt 4, Thunderbolt 3, USB4, and USB 3. Understanding their differences will help you make a more informed choice the next time you upgrade your device.

01
Comparison of Thunderbolt 4 and Thunderbolt 3
Thunderbolt is a unique technology developed by Intel, with some involvement from Apple. It is more of a brand name than a standard. Intel has been pushing this technology in Ultrabooks since 2011. Since its launch in 2020, Thunderbolt 4 has completely replaced Thunderbolt 3, supporting standards like USB4, DisplayPort 1.2, and PCIe. Thunderbolt 4 is compatible with almost all other devices, including all versions of Thunderbolt and USB.
Thunderbolt 4 continues to rely on the flexible USB-C form factor and has 40Gbps of bandwidth. Many of its features and minimum performance levels have surpassed those of Thunderbolt 3.
Compared to Thunderbolt 3, Thunderbolt 4 has improved minimum video support. The new standard now supports at least two 4K displays running at 60Hz or one 8K display running at 30Hz.
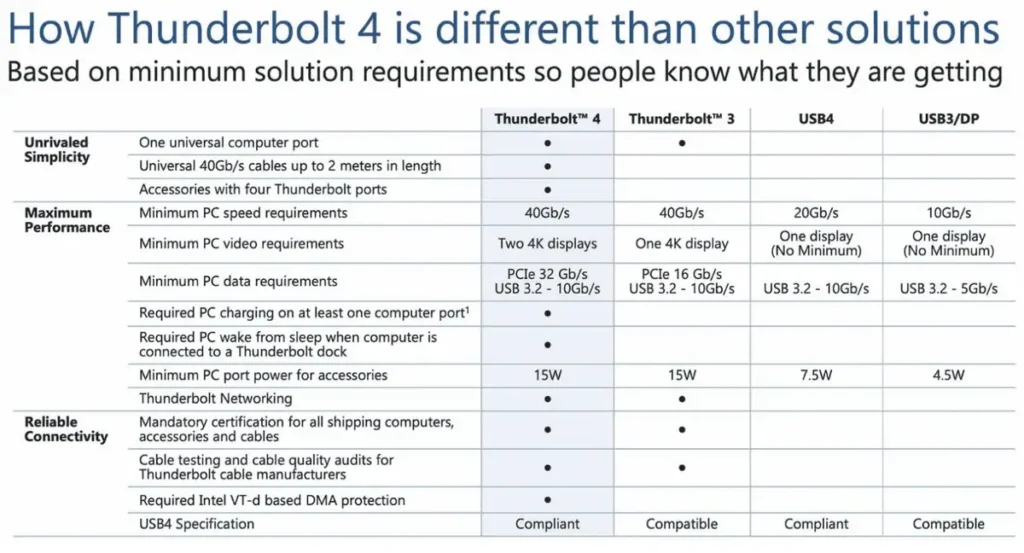
PCIe bandwidth requirements have doubled, increasing Thunderbolt 4 from Thunderbolt 3’s 16Gbps to 32Gbps. If you frequently use removable storage, you should theoretically be able to increase transfer speeds to around 3,000MB/s with Thunderbolt 4.
The best Thunderbolt 4 docking stations can offer up to three downstream Thunderbolt 4 ports and provide Direct Memory Access (DMA) protection through Intel’s virtualization technology to help counter threats.
02
USB4 is a high-performance USB standard

USB4 is the latest Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard named by the USB-IF. Previous USB versions progressed from USB 3.1 Gen 1 to USB 3.2 Gen 1 (5Gbps), and USB 3.1 Gen 2 to USB 3.2 Gen 2 (10Gbps).
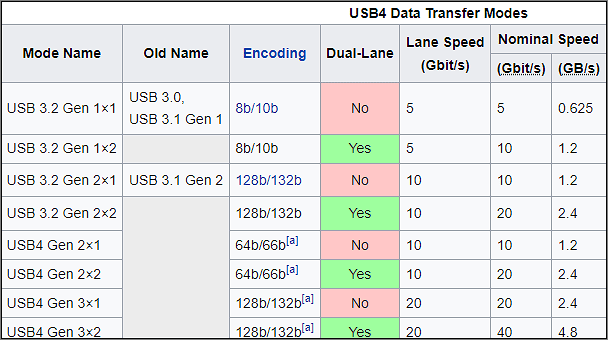
There’s also a newer USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 standard that can reach speeds of up to 20Gbps, provided the hardware supports it.
USB4 is now backward compatible with USB 2.0.
USB4 is built on Thunderbolt 3, so it has many of the same capabilities.
USB4 benefits from Intel largely abandoning the licensing of Thunderbolt 3. USB4 is based on Thunderbolt 3, so many of its features are similar. The best version of USB 3.0 reached speeds of 20Gbps, while USB4 matches Thunderbolt 3 and 4, each providing speeds of 40Gbps. USB4 strictly adopts the USB-C interface.
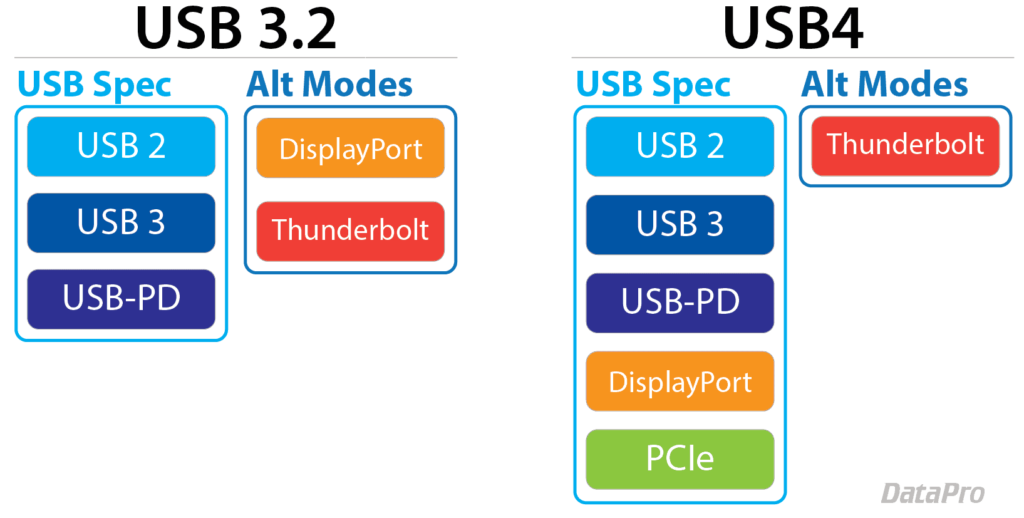
Previous USB versions divided bandwidth among all connected devices and relied on separate channels for data and video, with no crossover. USB4 allows lanes to share as needed, enabling you to reach the bandwidth limit. For example, with the best laptop docking station, USB4 can handle dual 4K displays or a single 5K display, and deliver up to 100W of charging power, the same as Thunderbolt 3.
The main takeaway is that USB4 aims to unify ports across devices. It’s time to move everything to USB-C with performance equivalent to Thunderbolt 3.
03
Differences between Thunderbolt 4 and USB4

USB4 has four different versions, but we mainly see USB4 Gen 2×2 and USB4 Gen 2×3, known as USB4 20Gbps and USB4 40Gbps, respectively.
USB4 only needs to reach 20Gbps and doesn’t have to support a minimum display resolution. Data transfer just needs to reach at least 10Gbps via USB 3.2. In contrast, Thunderbolt 4 ensures USB 3.2 reaches 10Gbps and provides 32Gbps PCIe performance.

The power requirements for USB4 ports are reduced to a minimum of 7.5W, while Thunderbolt 4 guarantees 15W.
Thunderbolt 4 and USB4 are compatible with each other, but Thunderbolt 4 ensures a specific level of performance.
04
Thunderbolt 5 on the Horizon
Thunderbolt 5 is expected to appear in some devices in 2024, bringing significant improvements over the previous generation. Intel outlined the anticipated improvements in the chart below.
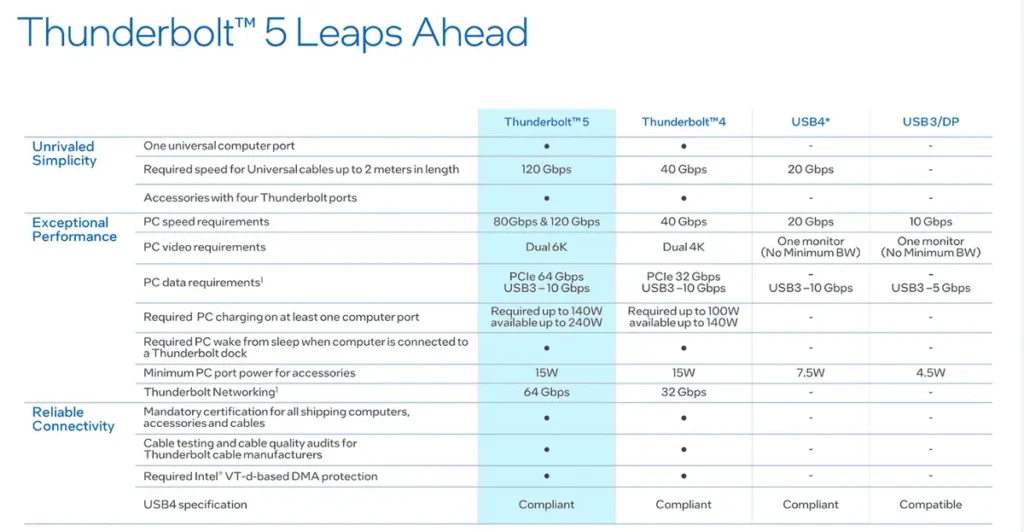
The most significant change is the massive increase in bandwidth, doubling Thunderbolt 4’s 40Gbps capacity. The new standard offers 120Gbps, with flexible bandwidth that can handle up to 80Gbps bidirectional transmission or 120Gbps sending and 40Gbps receiving simultaneously.
Thunderbolt 5 will offer more external display support, capable of running up to three external displays with high resolution and refresh rates on a single cable. Thunderbolt 5 can also handle up to 240W of charging power back to the host PC, easily exceeding Thunderbolt 4’s current 100W limit. This should make it more suitable for power-hungry gaming laptops and workstations.
Thunderbolt 5 will allow for easy connection to external GPUs. Even if you don’t have an AI PC, you can connect a dedicated GPU, which is also great for gaming.
Thunderbolt 5 will be compatible with USB4 and backward compatible with older Thunderbolt standards (though performance will be reduced when connected to PCs that don’t have Thunderbolt 5).
Related:
- USB4 vs Thunderbolt 4: Which Interface Reigns Supreme?
- HDMI or DisplayPort? Ultimate Comparison Guide

Disclaimer: This article is created by the original author. The content of the article represents their personal opinions. Our reposting is for sharing and discussion purposes only and does not imply our endorsement or agreement. If you have any objections, please contact us through the provided channels.








