USB4 and Thunderbolt 4 are currently the two most representative high-speed interfaces in the transmission field, both supporting transfer rates of up to 40Gbps.
USB4 was created by the USB standardization organization—USB-IF, while Thunderbolt 4 was developed by technology giants like Intel and Apple. Although these two high-performance interfaces are not in direct opposition, they are inevitably compared.

In today’s content, let’s discuss together: USB4 vs Thunderbolt 4, which is the stronger transmission interface?
01
USB4: Universal and Compatible
The USB4 interface integrates multiple transmission technologies, including PCI Express data transmission protocol, USB 3.2 transmission protocol, and DisplayPort video transmission protocol. USB4 combines these three protocols through a “tunneling protocol,” which has resulted in the interface’s excellent versatility.
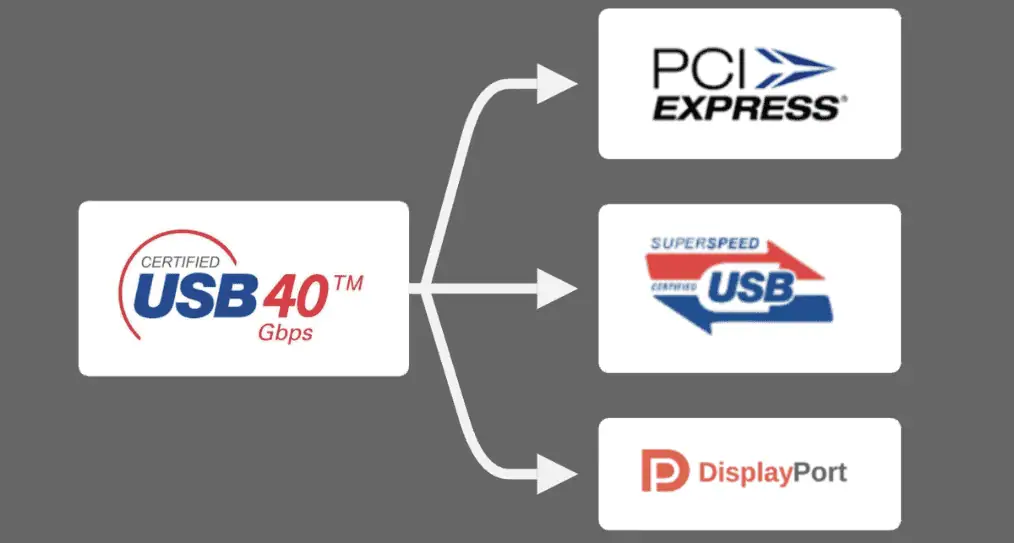
USB4, which merges multiple protocols, supports not only data transmission but can also be used as a video interface. Notably, USB4 also integrates the PD charging protocol, supporting up to 100W of fast charging.
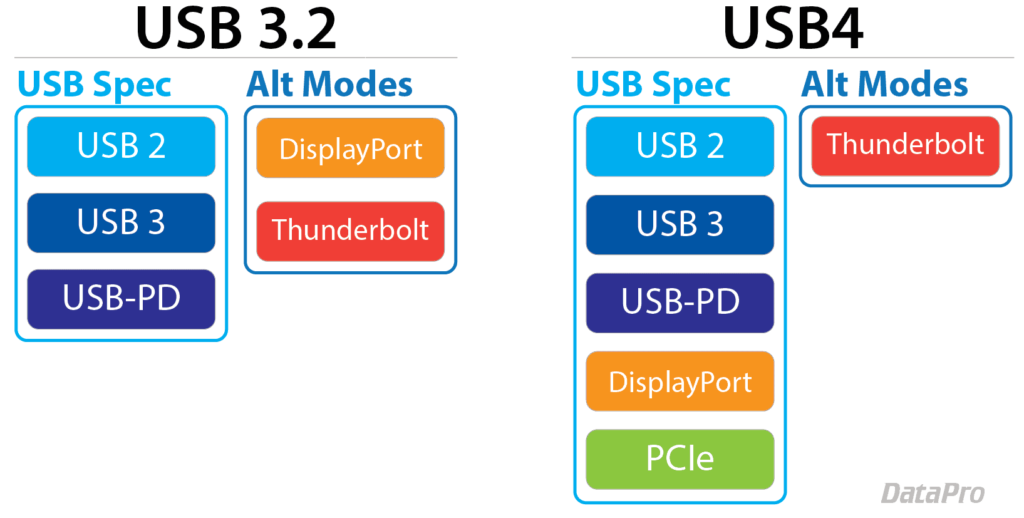
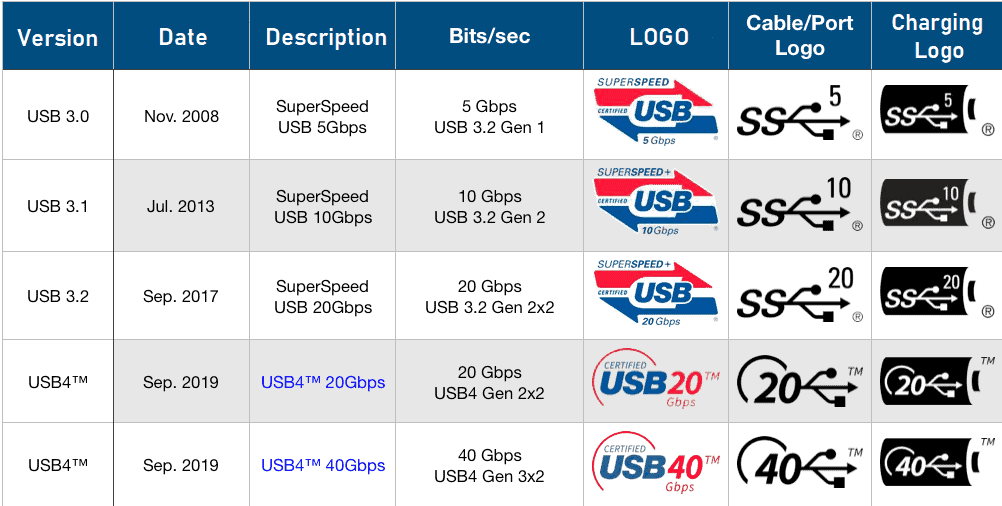
In the data transmission segment, USB4 achieves a bandwidth of 40 Gbps, the fastest speed among transmission interfaces in laboratory testing data. Currently, the mainstream USB 3.1 interface has a speed of 10Gbps, while USB4’s data transmission rate reaches four times that of the former.
Thanks to its ultra-high transmission rate, USB4 is also used in solid-state drive enclosures. Its 40Gbps transmission bandwidth can fully utilize the full rate advantages of PCIE 3.0, even PCIE 4.0 solid-state drives, meeting some users’ needs for ultra-high-speed data transmission.
Besides its strong data transmission capabilities, USB4’s performance with external display devices is also excellent, supporting up to 8K/60Hz displays, and is compatible with 4K, 2K, and 1080P resolution devices. Even ultra-high resolution and refresh rate esports monitors can meet the video transmission needs using a USB4 interface.
USB4 can perform high-speed data transmission and be used as a video interface, and supports up to 100W of PD fast charging standard, reflecting its multi-functional integration characteristics. In recent years, new laptops and NUC mini hosts have widely adopted the USB4 interface.
The USB4 interface uses a Type-C form factor design, allowing USB4 devices to perform multiple functions such as data transmission, video output, and power charging through a single full-featured Type-C cable, greatly simplifying product interface design and cable management.
02
Thunderbolt 4: Breakthrough in transmission performance
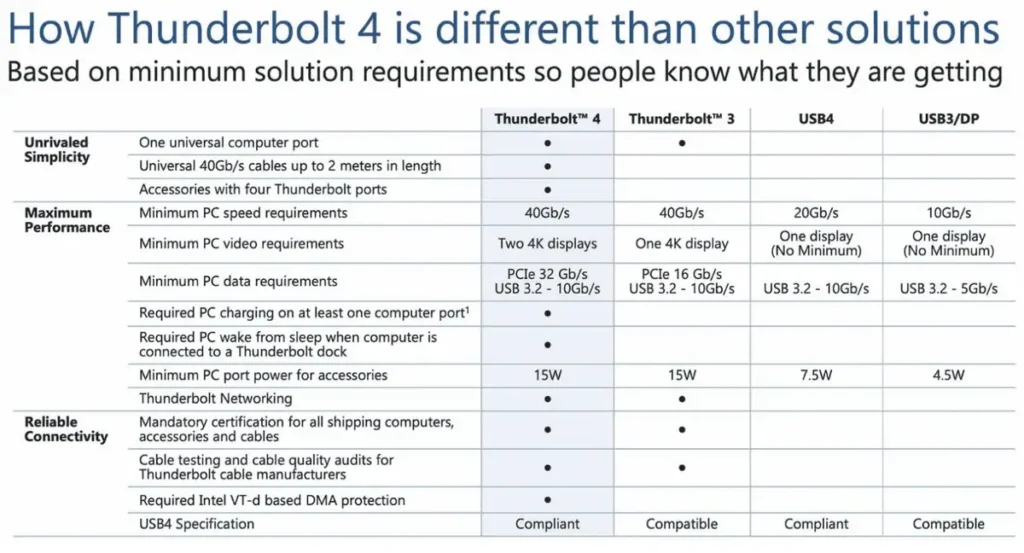
The Thunderbolt 4 interface, as a high-speed transmission technology jointly advanced by Intel and Apple, has evolved to its fourth generation, maintaining the same 40Gbps transmission bandwidth as its predecessor, Thunderbolt 3. It also serves as an “all-in-one” interface, encompassing data transfer, video output, and fast charging.
Thunderbolt 4’s high bandwidth is particularly evident in its performance in ultra-high-speed data transfers, where it can transmit a 50GB high-definition movie in just 10 seconds.
Thunderbolt 4’s most impressive feature is its video transmission capability. It not only supports connecting to an 8K/60Hz display but also supports the simultaneous use of two 4K resolution monitors. For gamers, media workers, and other user groups with a high demand for display quality, Thunderbolt 4 undoubtedly provides a superior viewing experience.
In terms of charging, Thunderbolt 4 supports 100W PD fast charging, meeting the rapid charging needs of high-performance devices.
03
USB4 compared to Thunderbolt 4
USB4 and Thunderbolt 4 share the same physical form, both using the USB-C interface. However, there are some detailed differences in their actual functions and user experience.
Firstly, in terms of universal compatibility, the USB4 interface is used in a broader range of end products compared to the Thunderbolt 4 interface. USB4 is an open, royalty-free interface, whereas using the Thunderbolt 4 interface requires the payment of royalties. Therefore, devices that use the USB4 interface tend to be more cost-effective compared to those with Thunderbolt 4.

On the other hand, end devices that use the Thunderbolt 4 interface need to incorporate Intel’s Thunderbolt controller chips, such as the JHL8440 or JHL8540 chips, which also carry a relatively high cost. Thus, Thunderbolt 4 interfaces are commonly found in high-priced flagship laptops.
Additionally, another difference between USB4 and Thunderbolt 4 lies in the minimum data transfer rate.
Although both can achieve up to 40Gbps transmission rates, their “minimum data transfer rates” differ. USB4 has a minimum data transfer rate of 10Gbps, approximately 1.25GB/s; Thunderbolt 4’s minimum data transfer rate is 32Gbps, approximately 4GB/s.
04
In Conclusion
There are virtually no differences between USB4 and Thunderbolt 4 in terms of functionality, whether in data transfer, video transmission, or charging power; the experience is essentially the same.
The core difference lies in the cost of devices using these interfaces. Devices with the USB4 interface are more cost-effective, while those with the Thunderbolt 4 interface are relatively more expensive. Additionally, devices that incorporate the Thunderbolt 4 interface have a higher “minimum” data transfer rate, which ensures better data transmission performance, marking a key advantage over USB4.

This price difference results in USB4 having a wider range of applications and higher consumer acceptance. Although Thunderbolt 4 products are more expensive, their higher minimum data transfer rates make them suitable for consumers seeking ultimate performance and efficiency.
Related:

Disclaimer: This article is created by the original author. The content of the article represents their personal opinions. Our reposting is for sharing and discussion purposes only and does not imply our endorsement or agreement. If you have any objections, please contact us through the provided channels.








